

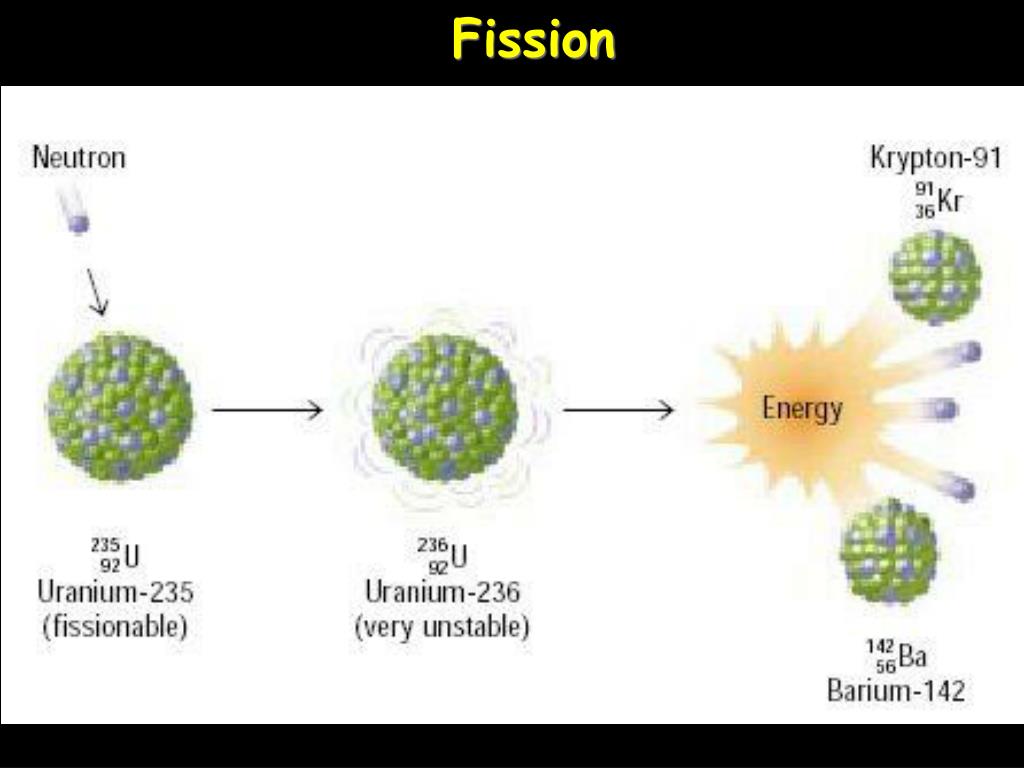
When one piece in the form of a bullet is fired into the second piece, the critical mass is exceeded and a chain reaction is produced.Īn important obstacle to the U-235 bomb is the production of a critical mass of fissionable material. The original design required two pieces of U-235 below the critical mass. When the critical mass reaches a point at which the chain reaction becomes self-sustaining, this is a condition known as criticality. The minimum mass needed for the chain reaction to occur is called the critical mass. In addition, the uranium sample must be massive enough so a typical neutron is more likely to induce fission than it is to escape. To produce a controlled, sustainable chain reaction, the percentage of U-235 must be increased to about 50 % 50 %. (These discoveries were taking place in the years just prior to the Second World War and many of the European physicists involved in these discoveries came from countries that were being overrun.) Natural uranium contains 99.3 % 99.3 % U-238 and only 0.7 % 0.7 % U-235, and does not produce a chain reaction. The possibility of a chain reaction in uranium, with its extremely large energy release, led nuclear scientists to conceive of making a bomb-an atomic bomb. Control energy production in a nuclear reactor. View a simulation on nuclear fission to start a chain reaction, or introduce nonradioactive isotopes to prevent one. If this vibration is violent enough, the nucleus divides into smaller nuclei and also emits two or three individual neutrons. A neutron fired into a uranium nucleus can set the nucleus into vibration. In particular, forces between nucleons at the surface of the nucleus result in a surface tension similar to that of a water droplet. The analogy works because short-range forces between nucleons in a nucleus are similar to the attractive forces between water molecules in a water droplet. According to this model, firing a neutron at a nucleus is analogous to disturbing a droplet of water ( Figure 10.19). Niels Bohr and John Wheeler developed the liquid drop model to understand the fission process. This energy is carried away by high-energy neutrons. Therefore, a fission reaction results in a drop in the average energy of a nucleon. This means that nucleons in the nuclear fragments are more tightly bound than those in the U-235 nucleus. The BEN value for uranium ( A = 236 ) ( A = 236 ) is slightly lower than its daughter nuclei, which lie closer to the iron (Fe) peak. Figure 10.18 In this graph of fission fragments from U-235, the peaks in the graph indicate nuclei that are produced in the greatest abundance by the fission process.Įnergy changes in a nuclear fission reaction can be understood in terms of the binding energy per nucleon curve ( Figure 10.7).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
